How to Optimize Ecommerce Logistics in 2024

When customers place an online order with your business, 68% of them expect their package to arrive at their doorstep within three days of placing the order. If you fail to meet that expectation, it can have a severe impact on their experience with your brand. According to one survey, 98% of shoppers consider shipping as a factor that impacts brand loyalty.
For ecommerce businesses that rely on shipping to get orders to customers, effective shipping and delivery are vital for business success. To guarantee deliveries arrive at customers’ doorsteps without any hiccups, managers should focus on logistics practices. Understanding what ecommerce logistics is and what it looks like for your business will help improve your delivery efficiency. And the more efficient your deliveries are, the happier your customers will be.
Jump to the section that you’re most interested in:
- What Is Ecommerce Logistics?
- 4 Steps in Ecommerce Logistics
- 3 Different Approaches to Ecommerce Logistics
- How to Optimize Ecommerce Logistics
- Streamline Last Mile Delivery With OptimoRoute
- FAQs About Ecommerce Logistics
What Is Ecommerce Logistics?
Ecommerce logistics refers to all of the processes that online retail organizations use to fill customer orders and deliver them to their final destination. This is vital for ecommerce businesses that don’t have a storefront for customers to visit when making purchases or returns. But ecommerce logistics is about more than getting packages to customers. A good logistics strategy will encompass the beginning of the process when an order is placed and flow through the rest of the process. This requires logistics planners to account for a variety of factors, including where to store products, how to fill orders, and how to complete deliveries.
4 Steps in Ecommerce Logistics
Ecommerce logistics includes a variety of tasks, which can be broken down into four primary logistics steps: inventory management, order management, last mile delivery, and reverse logistics.
Inventory management and warehousing
Ecommerce logistics begins even before a company receives an order. To complete orders when they come in, businesses need to have enough inventory to meet the demand. This requires logistics planners to look at sales trends to understand what their least and most popular products are. Managers can use this knowledge to ensure they have the right stock on hand. And once the right stock is on hand, it needs to be warehoused efficiently. This means placing popular items in areas that are easiest to access.
New small businesses typically have a very small inventory while they grow their business, which makes inventory and warehouse management relatively easy to handle. However, larger organizations often have bigger inventories and a higher volume of sales. This requires larger businesses to use more complex warehouse management practices. For example, a large ecommerce retailer like Amazon has to coordinate shipments of products to individual warehouses around the world so that distribution centers can fill orders and guarantee its Prime shipping lives up to the promise of one- and two-day delivery.

Order management and fulfillment
The order management process begins when a customer makes an online purchase. After receiving the order, the organization will next need to double-check that all of the ordered products are available in inventory by either locating the products in an electronic inventory system or physically finding them in the warehouse. Once the product is located, it gets packaged and prepared for delivery. This final stage of the order management process is known as order fulfillment, and the faster the process is, the more likely it is that the delivery will be on time.
Last mile delivery
The next, and sometimes final, step in ecommerce logistics is last mile delivery. This is the part of the process that takes a package from the warehouse or shipping center and delivers it directly to the customer. This is one of the most important stages in logistics for ecommerce businesses because it has the most direct impact on the customer. Improper handling during this stage can lead to broken products, while poor scheduling can create long delivery times that negatively impact how customers think about your brand. For smooth deliveries, businesses should turn to last mile delivery software to help automate and streamline the process.
Reverse Logistics
Online retailers need to be proactive in creating a plan for how they will handle returns as part of their planning. Known as reverse logistics, this step covers any part of the logistics process where products move from the final destination, the customer, back to the distribution center. What this looks like can vary from business to business, depending on factors like what products the business sells and how it delivers them. This might mean picking up returns from the customer directly or providing a shipping label for easy returns.
3 Different Approaches to Ecommerce Logistics
The specific logistics practices an ecommerce company uses look different depending on the industry the business operates in and what type of products it sells online. Other factors can also have an impact on logistics, including the budget for shipping and delivery as well as the size of the team. The three most common approaches to ecommerce logistics are handling the entire process in-house, outsourcing to a third party, and dropshipping.
In-house fulfillment and self-delivery
Handling logistics in-house gives organizations complete control. In-house order fulfillment gives managers peace of mind because they can ensure that every order is filled efficiently and correctly. Meanwhile, self-delivery helps businesses provide the best customer service by allowing them to train their own delivery teams on how to handle packages and interact with customers.
To handle logistics in-house, ecommerce businesses need to hire a team to complete all of the logistics tasks. This includes hiring warehouse staff for order fulfillment as well as a delivery team and managerial staff to oversee it all. This is typically the method that new businesses use while they are getting operations off the ground. But it is also a good option for businesses with a high volume of orders and large inventories to manage, which can be too expensive to outsource to a third party.
Outsourcing to a 3PL
Third-party logistics (3PL) sees businesses outsource their logistics to a dedicated logistics company. Relying on a 3PL partner comes with its own benefits, including handling all of the essential and stressful logistics steps that take time away from managers, such as planning delivery routes. Many 3PLs offer customizable and scalable service options, which means that businesses only pay for the services that they need. However, logistics providers can also be expensive, which means they may not be a good option for businesses with small budgets.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is more than just an approach to logistics. It’s a business model in which ecommerce businesses operate as a storefront that sells other companies’ products. When a customer purchases a product, the ecommerce business facilitates the transaction by purchasing the product from a third party and shipping it to the customer. This approach lowers costs by eliminating warehousing and shipping costs. But it also means that business owners have very little control over the order fulfillment or shipping process, which creates many risks. For example, say the third party you work with fills an order incorrectly or fails to ship the product. Since customers are interacting with your business, the failings of the logistics partner will reflect poorly on your brand.
How to Optimize Ecommerce Logistics
Shipping is a make-or-break factor for more than half of consumers. In fact, one study found that 58% of customers stopped shopping with a brand as a direct result of a negative shipping experience. This makes logistics a critical factor, and optimizing your practices will boost efficiency, provide the best shipping options, and provide a positive experience for your customers.
Make sure to forecast inventory needs
The cost of renting a warehouse has been on the rise since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. A recent report predicts that costs will continue to soar through 2023. To help minimize this cost for your business, you should optimize your inventory to minimize the amount of warehouse space you pay for. To do this, you need to use a process called inventory forecasting to assess how much inventory you need to store.
How to forecast inventory needs:
- Determine lead time by calculating how much time it takes your team to fill an order once it has been received. Assess the data from the last four to six order periods to get an average lead time for your organization.
- Look at past sales records and analyze the data to identify sales trends. Look specifically at which products you sell the most of and when customers are most likely to buy them.
- Use the trends and past sales numbers to determine how much inventory you need to keep on hand to fill your average daily orders.

Set reorder points and mandatory inventory minimums
A reorder point is the point at which you need to restock your inventory. It’s indicated by the inventory minimum. When inventory hits this level, it signals that it’s time to reorder, so inventory never runs low. However, your business inventory minimum will fluctuate depending on shopping trends and seasonality. So, logistics planners will need to regularly assess inventory minimums to set reorder points.
How to set reorder points:
- Calculate how much inventory you need to fill average daily orders by multiplying your lead time by your average number of daily sales. This number is known as “lead order demand.”
- Set your safety stock. Your safety stock is a reserve inventory that you can dip into if sales are higher than your predictions, ensuring you can fill orders without delay.
- Add your lead order demand to your safety stock. This number is your inventory minimum.
Use logistics management systems
Regularly assessing your prior sales data to calculate and optimize your inventory is difficult and time consuming. And relying on a single person to do the job leaves plenty of opportunities for human error if the planner makes a simple miscalculation. To avoid this, ecommerce businesses should rely on logistics management systems to automate tasks like warehouse management, supply chain management, and delivery route planning.
Focus on efficient and cost-effective last mile delivery
Last mile delivery accounts for more than half of the total cost of shipping. This is when a package leaves the shipping destination and arrives at the customer’s doorstep, which means more stops and more complex delivery routes. Maximizing the efficiency of your final mile logistics ensures that you keep your costs low.
To improve the efficiency of your last mile delivery, planners can use route optimization, a process that finds the most efficient routes. Route optimization requires planners to account for a variety of factors, including the number of scheduled deliveries, where each delivery is located, how many packages can fit on a vehicle, and which drivers are available. This is a difficult process to do manually, making route optimization tools like OptimoRoute a valuable tool for ecommerce businesses.
Streamline Last Mile Delivery With OptimoRoute
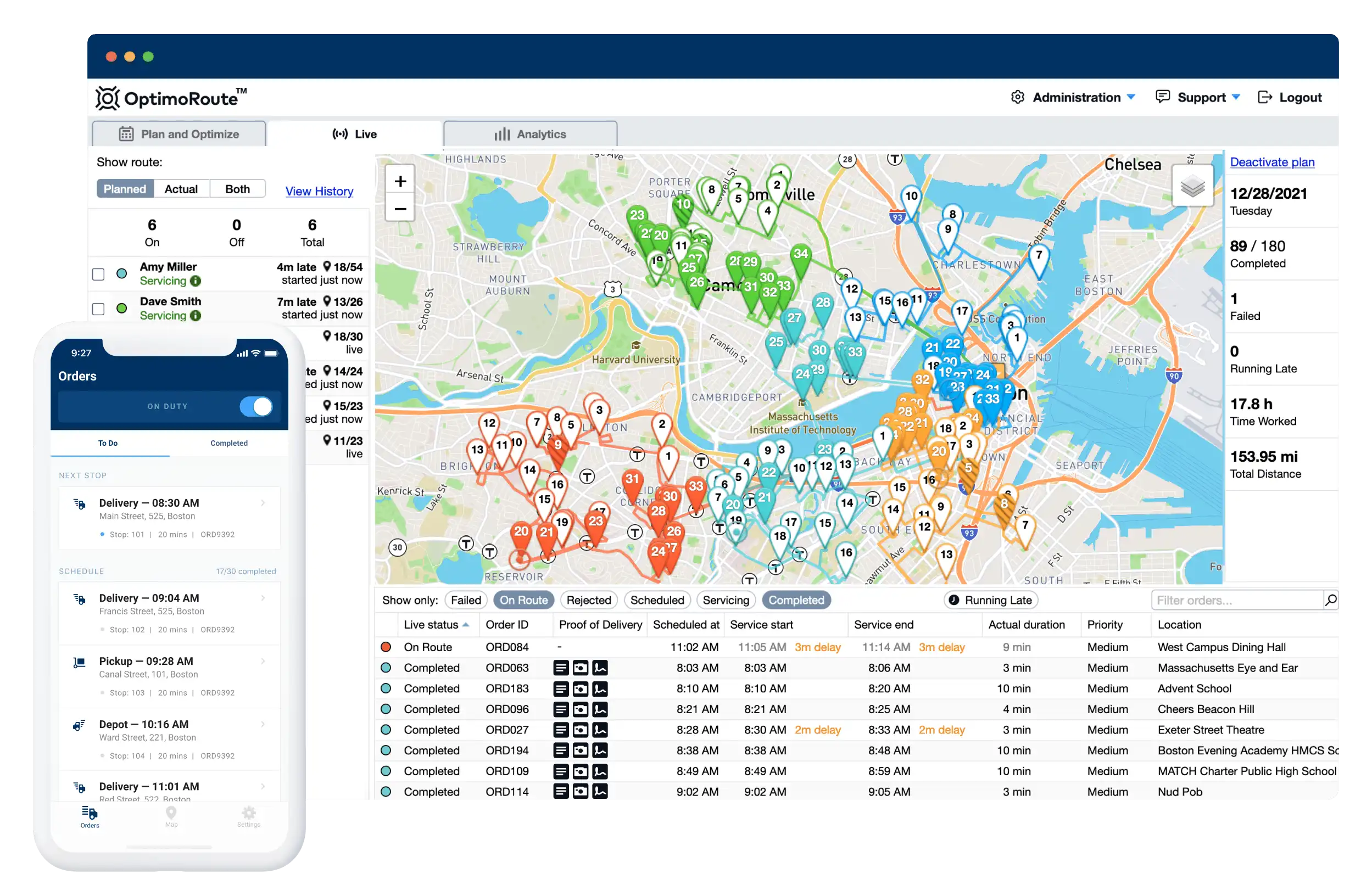
Relying on a planning tool like OptimoRoute isn’t just good for your logistics operations, it’s good for your bottom line. That’s because 78% of consumers are more willing to buy from a brand that uses sophisticated technology in its supply chain. The reason is that relying on technology drastically reduces human error, giving customers peace of mind that their packages will arrive at the right place on time. OptimoRoute helps improve logistics in your supply chain by offering a variety of features to help streamline your delivery operations. Some of those features include:
- Automated Planning: Automatically generate delivery routes up to five weeks into the future. When changes occur, OptimoRoute can adjust the route to accommodate with just a few clicks.
- Pickup and Delivery: Build routes that include stops for both deliveries and pickup orders to streamline reverse logistics.
- Realtime Order Tracking: Improve the customer experience by sending customers updates about when their order will arrive.
Start your free, 30-day trial today and see how OptimoRoute can help optimize your ecommerce business logistics practices.
FAQs About Ecommerce Logistics
In this section, we’ll answer three of the most frequently asked questions about ecommerce logistics.
What is the difference between logistics and distribution?
Logistics encompasses the full scope of an organization’s supply chain processes. Distribution is one piece of logistics that specifically refers to the transportation of products to distribution centers, warehouses, and their final destination.
Does OptimoRoute help with ecommerce logistics?
OptimoRoute helps streamline last mile delivery and reverse logistics, which are two essential steps of ecommerce logistics.
How do I start a logistics company?
To start a logistics company, you must first research logistics and learn what certifications and licenses you need. Then you’ll need to complete a variety of tasks, including picking a business name, registering your business, taking out a small business loan to fund your enterprise, and marketing your business to attract customers.
Try OptimoRoute™ for Free
No installation or credit card required


